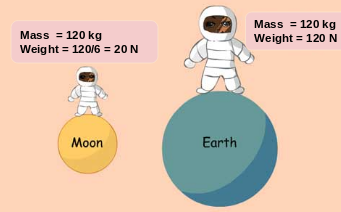
The weight of an object on the earth is the force with which the earth attracts the object. In the same way, the weight of an object on the moon is the force with which the moon attracts that object.
The mass of the moon is less than that of the earth. Due to this, the moon exerts a lesser force of attraction on objects. Let the mass of an object be m. Let its weight on the moon be Wm. Let the mass of the moon be Mm and its radius be Rm .
By applying the universal law of gravitation, the weight of the object on the moon will be
Wm = G Mm x m / Rm2
Let the weight of the same object on the earth be We. The mass of the earth is M and its radius is R.
we have, We = G M x m / R2
Substituting the values from , we get
Wm = G X 7.36 X 1022 kg x m / (1.74 X 106 m )2
Wm = 2.431 x 1010G x m
We = 1.474 x 1011 G x m
Dividing Eq. (1) by Eq. (2), we get
Wm / We = 2.431 x 1010G x m / 1.474 x 1011 G x m
Wm / We = 0.165 = 1 / 6
Weight of the object on the moon / Weight of the object on the earth = 1 / 6
Weight of the object on the moon = (1/6) × its weight on the earth.
