The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to break-down glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water, and some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen .
In all cases, the first step is the break-down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process takes place in yeast during fermentation. Since this process takes place in the absence of air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration.
The breakdown of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This process breaks up the three-carbon pyruvate molecule to give three molecules of carbon dioxide. The other product is water. Since this process takes place in the presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration.
The release of energy in this aerobic process is a lot greater than in the anaerobic process. Sometimes, when there is a lack of oxygen in our muscle cells, another pathway for the breakdown of pyruvate is taken. Here the pyruvate is converted into lactic acid which is also a three-carbon molecule. This build-up of lactic acid in our muscles during sudden activity causes cramps.

The energy released during cellular respiration is immediately used to synthesise a molecule called ATP which is used to fuel all other
activities in the cell. In these processes, ATP is broken down giving rise to a fixed amount of energy which can drive the endothermic reactions taking place in the cell.
Since the aerobic respiration pathway depends on oxygen, aerobic organisms need to ensure that there is sufficient intake of oxygen. We
have seen that plants exchange gases through stomata, and the large inter-cellular spaces ensure that all cells are in contact with air. Carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged by diffusion here. They can go into cells, or away from them and out into the air. The direction of diffusion depends upon the environmental conditions and the requirements of the plant. At night, when there is no photosynthesis occurring, CO2 elimination is the major exchange activity going on. During the day, CO2 generated during respiration is used up for photosynthesis, hence there is no CO2 release. Instead, oxygen release is the major event at this time.
Animals have evolved different organs for the uptake of oxygen from the environment and for getting rid of the carbon dioxide produced. Terrestrial animals can breathe the oxygen in the atmosphere, but animals that live in water need to use the oxygen dissolved in water.
Since the amount of dissolved oxygen is fairly low compared to the amount of oxygen in the air, the rate of breathing in aquatic
organisms is much faster than that seen in terrestrial organisms. Fishes take in water through their mouths and force it past the gills where the dissolved oxygen is taken up by blood.
Terrestrial organisms use the oxygen in the atmosphere for respiration. This oxygen is absorbed by different organs in different animals. All these organs have a structure that increases the surface area which is in contact with the oxygen-rich atmosphere. Since the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide has to take place across this surface, this surface is very fine and delicate. In order to protect this surface, it is usually placed within the body, so there have to be passages that will take air to this area. In addition, there is a mechanism for moving the air in and out of this area where the oxygen is absorbed.
In human beings , air is taken into the body through the nostrils. The air passing through the nostrils is filtered by fine hairs that line the passage. The passage is also lined with mucus which helps in this process. From here, the air passes through the throat and into the lungs. Rings of cartilage are present in the throat. These ensure that the air-passage does not collapse.
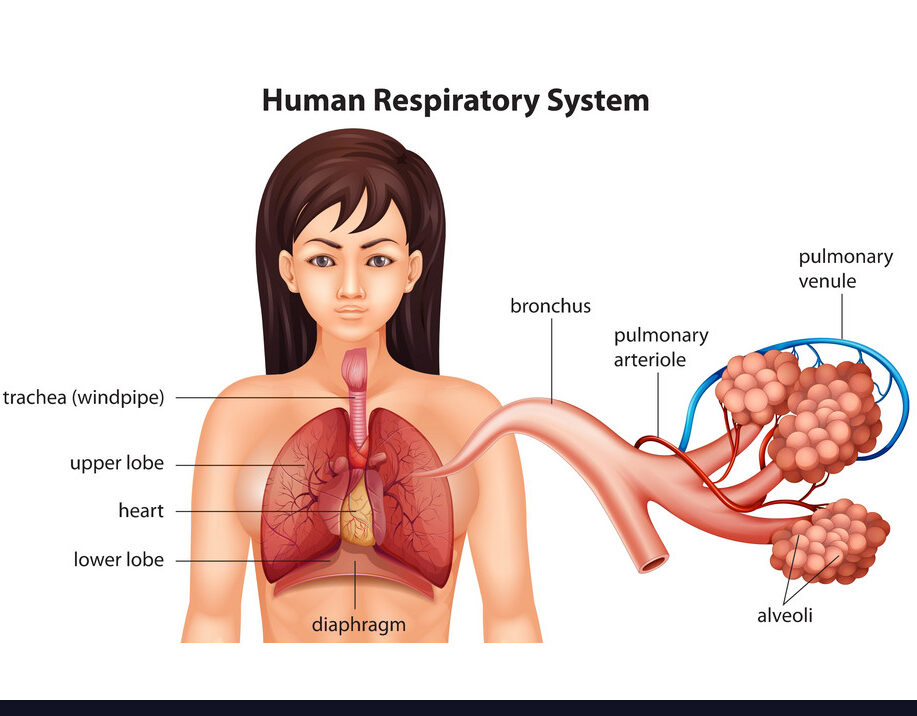

Within the lungs, the passage divides into smaller and smaller tubes which finally terminate in balloon-like structures which are called alveoli (singular–alveolus). The alveoli provide a surface the exchange of gases can take place. The walls of the alveoli contain an extensive network of blood vessels.
when we breathe in, we lift our ribs and flatten our diaphragm, and the chest cavity becomes larger as a result. Because of this, the air is sucked into the lungs and fills the expanded alveoli.
The blood brings carbon dioxide from the rest of the body for release into the alveoli, and the oxygen in the alveolar air is taken up by the blood in the alveolar blood vessels to be transported to all the cells in the body. During the breathing cycle, when air is taken in and let out, the lungs always contain a residual volume of air so that there is sufficient time for oxygen to be absorbed and for carbon dioxide to be released.
When the body size of animals is large, the diffusion pressure alone cannot take care of oxygen delivery to all parts of the body. Instead, respiratory pigments take up oxygen from the air in the lungs and carry it to tissues which are deficient in oxygen before releasing it. In human beings, the respiratory pigment is haemoglobin which has a very high affinity for oxygen. This pigment is present in the red blood corpuscles. Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen is and hence is mostly transported in the dissolved form in our blood.
