Solution :
Human female reproductive organ
The primary and auxiliary sex organs are all part of the female reproductive system. The primary sex organs in females are two ovaries, which also emit female sex hormones including progesterone and oestrogen in addition to producing ova or eggs. The uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina are among the other accessory sex organs. The labia minora, labia majora, and clitoris make up the external genitalia. Despite not being regarded as genital organs, the mammary glands are significant glands in the female reproductive system.
Labelled Diagram of Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system comprises of parts which are both internal and external to the body.
External Reproductive Parts
The external parts of the female reproductive system include:
Labia majora:The other external reproductive organs are encased and protected by it. The labia majora is comparable to the male scrotum and is described as being oversized and fat. It has glands that secrete both perspiration and oil. After adolescence, the labia majora begin to grow hair.

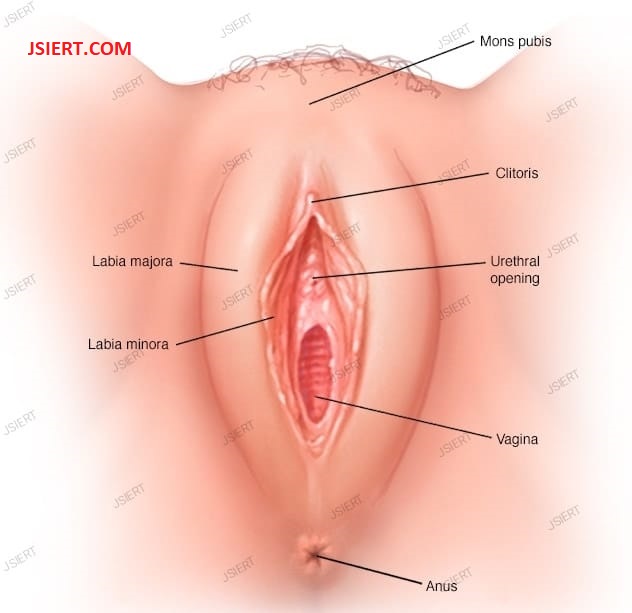
Labia minora: These lips, which are roughly 2 inches wide and are translated as “little lips,” can be exceedingly tiny. Just inside the labia majora, the labia minora rest. It encircles the urethra’s and the vagina’s main openings.
Bartholin’s glands: These glands are situated next to the vaginal opening and are in charge of controlling fluid discharge.
Clitoris: The clitoris, a little, delicate protrusion similar to the penis in the male reproductive system, is where the labia minora meet. Prepuce is the name of the skin fold that covers this portion of the female reproductive system. The clitoris is responsive to stimuli and has the ability to become erect, just like the male penis.
Internal Reproductive Parts
The internal parts of the female reproductive system include:
Vagina: The cervix is connected to the outside of the body by a canal. It may also be referred to as the birth canal.
Womb or Uterus: It is a hollow, pear-shaped organ that serves as the growing foetus’ “home.” The uterus also divides into two halves, the corpus and the cervix. The corpus may readily expand to accommodate a growing child.
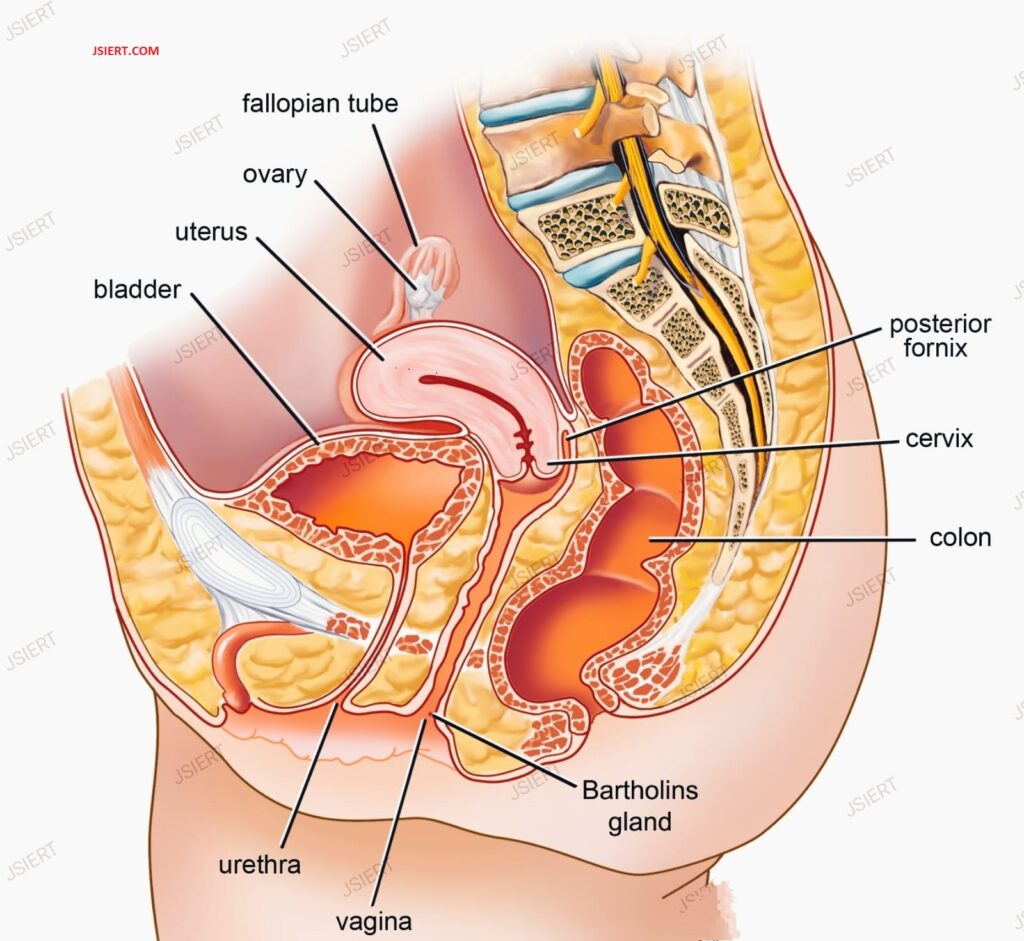
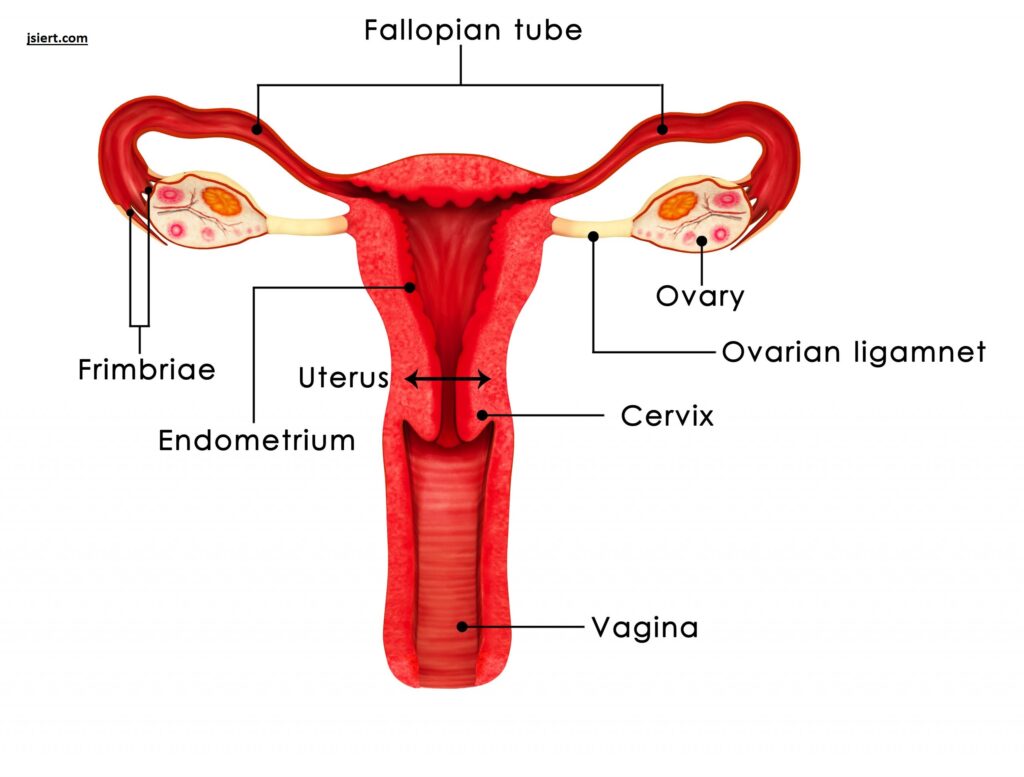
Ovaries: These tiny, oval-shaped glands are found on either side of the uterus. Hormones and eggs are produced by ovaries.
Fallopian tubes: The fallopian tubes are tiny tubes that connect to the top of the uterus. Egg cells go via the fallopian tubes like tunnels. To get the egg cells to the uterus, they move them from the ovaries.
Female Reproductive System: Its Importance
The creation of female egg cells, which are necessary for reproduction, is the main purpose of the female reproductive system. The term “ova” or “oocytes” refers to them. It’s critical to understand that the entire system is built to get the ova to the precise location of fertilisation. Furthermore, the fallopian tubes are typically where an egg becomes fertilised after coming into contact with a sperm.
The fertilised egg’s later stage is when it begins to embed itself in the uterine walls. The early stages of pregnancy officially start with this. The mechanism is designed to menstruate in the event that neither fertilisation nor implantation takes place. Additionally, female sex hormones, which are produced by the female reproductive system,
