The particles of a colloid are uniformly spread throughout the solution. Due to the relatively smaller size of particles, as compared to that of
a suspension, the mixture appears to be homogeneous. But actually, a colloidal solution is a heterogeneous mixture, for example, milk.

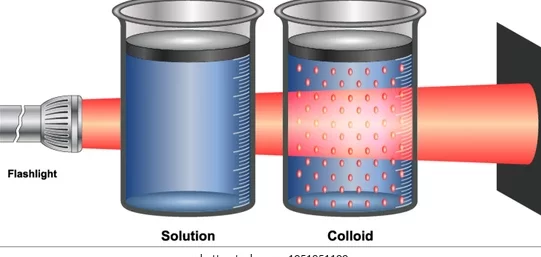
Because of the small size of colloidal particles, we cannot see them with naked eyes.
But, these particles can easily scatter a beam of visible light . This scattering of a beam of light is called the Tyndall effect after the name of the scientist who discovered this effect.
Tyndall effect can also be observed when a fine beam of light enters a room through a small hole. This happens due to the scattering of light
by the particles of dust and smoke in the air.
Tyndall effect can be observed when sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest. In the forest, mist contains tiny droplets
of water, which act as particles of colloid dispersed in air.
Properties of a colloid
• A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture.
• The size of particles of a colloid is too small to be individually seen by naked eyes.
• Colloids are big enough to scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible.
• They do not settle down when left undisturbed, that is, a colloid is quite stable.
• They cannot be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration. But, a special technique of separation known as centrifugation ,
can be used to separate the colloidal particles.
The components of a colloidal solution are the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium. The solute-like component or the dispersed particles in a colloid form the dispersed phase, and the component in which the dispersed phase is suspended is known as the dispersing medium. Colloids are classified according to the state (solid, liquid or gas) of the dispersing medium and the dispersed phase.
