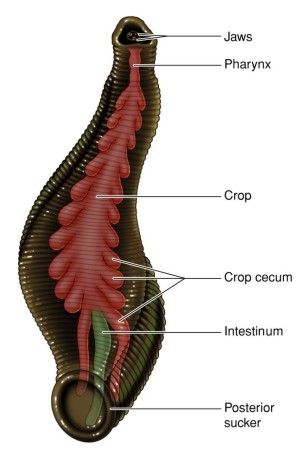
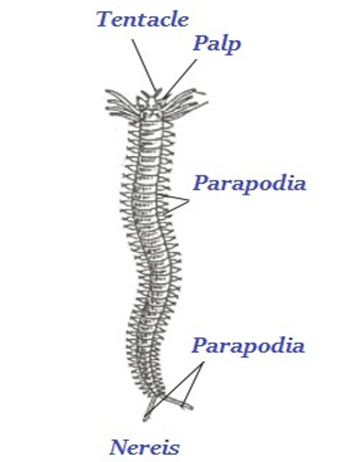

Annelid animals are also bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic, but in addition they have a true body cavity. This allows true organs to be packaged in the body structure. There is, thus, extensive organ differentiation.
This differentiation occurs in a segmental fashion, with the segments lined up one after the other from head to tail. These animals are found in a variety of habitats– fresh water, marine water as well as land. Earthworms and leeches are familiar examples
