Tissue culture
Definition :
“Tissue culture is the technique of growing cells and tissues in an artificial medium separate from the organism.”
What is Tissue Culture?
Plant fragments can be cultivated in a lab using the technique known as tissue culture. The use of the organs for tissue culture occurs often. Broth and agar are the media that are utilised to develop the culture.
The term “micropropagation” is another name for this method. Growing disease-free plants and increasing plant output in underdeveloped nations have both benefited from it. It merely needs a clean work environment, a greenhouse, skilled labour, and a nursery.
Oil palm, banana, eggplant, pineapple, rubber tree, tomato, sweet potato have been produced by tissue culture in the developing countries.
Types of Tissue Culture
Seed Culture
Embryo Culture
Callus Culture
Organ Culture
Protoplast Culture etc.
Steps of Tissue Culture
Following are the steps in tissue culture:
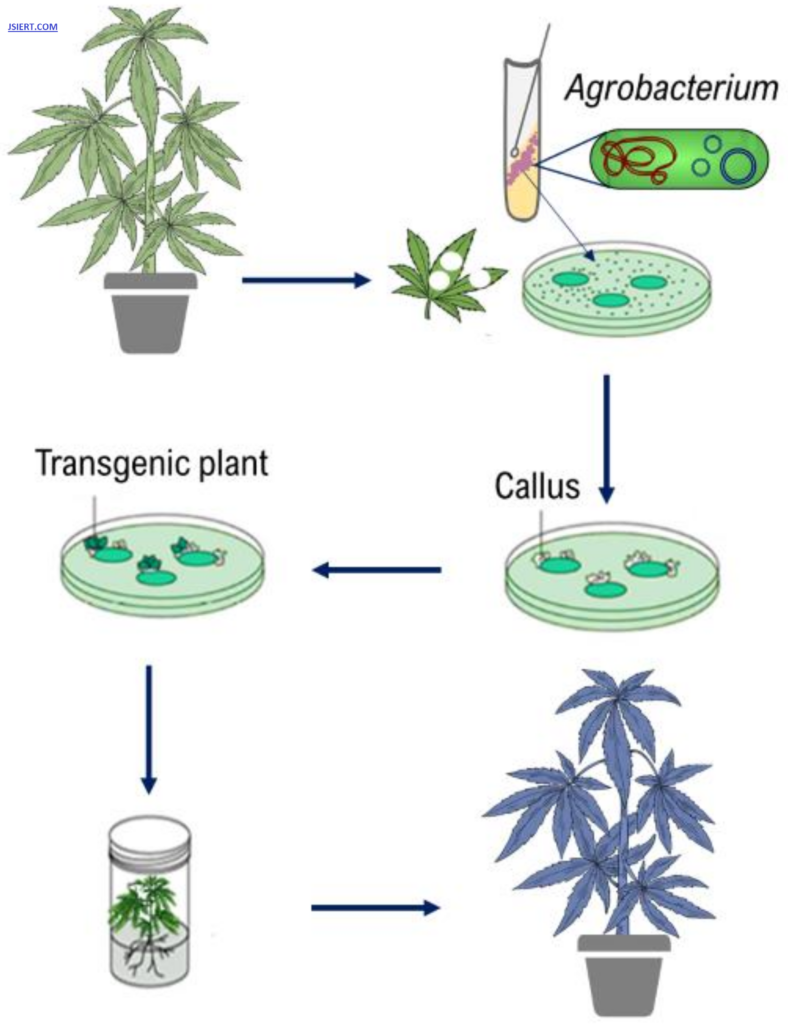
Initial Stage
The tissue is now introduced into the culture at this point. To avoid any process contamination, the desired tissue is acquired, added, and sterilised.
Phase of Multiplication
At this stage, the sterile explant is inserted into the medium that contains the necessary nutrients and growth regulators. They control cell division and multiplication. A callus is an undifferentiated cluster of cells.
Root Growth
The roots begin to grow. To start the creation of the roots, plant growth hormones are given. As a result, we get entire plantlets.
Shoot Formation
For the purpose of forming a shoot, plant growth hormones are injected, and the growth is tracked for a week.
Acclimatization
Once the plant begins to grow, it is moved into a greenhouse where it can mature in a climate-controlled setting. Finally, it is sent to the nurseries where it can develop in a natural habitat.
Advantages of Tissue Culture
(i)The following are some of the many benefits of the tissue culture technique:
(ii) With a minimal amount of plant tissue, the plantlets can be produced in a relatively short amount of time.
(iii) The newly created plants are devoid of illness.
(iv) No matter the season, the plants can be grown all year long.
(v) The tissue culture technique can be used to produce plants in small spaces.
(vi) The market is seeing an increase in the manufacturing of new types.
(vii) The cultivation of attractive plants like dahlias, chrysanthemums, orchids, etc. is done using this method.
Tissue Culture’s Importance
(i)Tissue culture is very important in biology due to its wide range of applications.
(ii) Tissues from both plants and animals can be used for cultivation. Animal tissue culture, for instance, aids in the preservation of an organ or tissue.
(iii) A plant’s genetic makeup can be altered through plant tissue culture, or a plant’s yield can simply be increased. Plants with desired traits can be created by genetically modifying the cells of the plants.
(iv) This method makes use of the plant’s quick tissue regeneration capacity. It creates clones, which are perfect copies of itself.
(v) It is a method for swiftly growing plants devoid of bulbs, seeds, or tubers.
(vi) By producing endangered species, it also aids in the preservation of plant biodiversity.
