Nephrons are the filtration units of the kidney, which are large in numbers.
As the urine moves down the tube, certain components of the original filtrate, including glucose, amino acids, salts, and a significant amount of water, are selectively reabsorbed.
The main components of Nephrons are
Glomerulus
Bowman’s Capsule
Long Renal Tube
Structure of Nephron
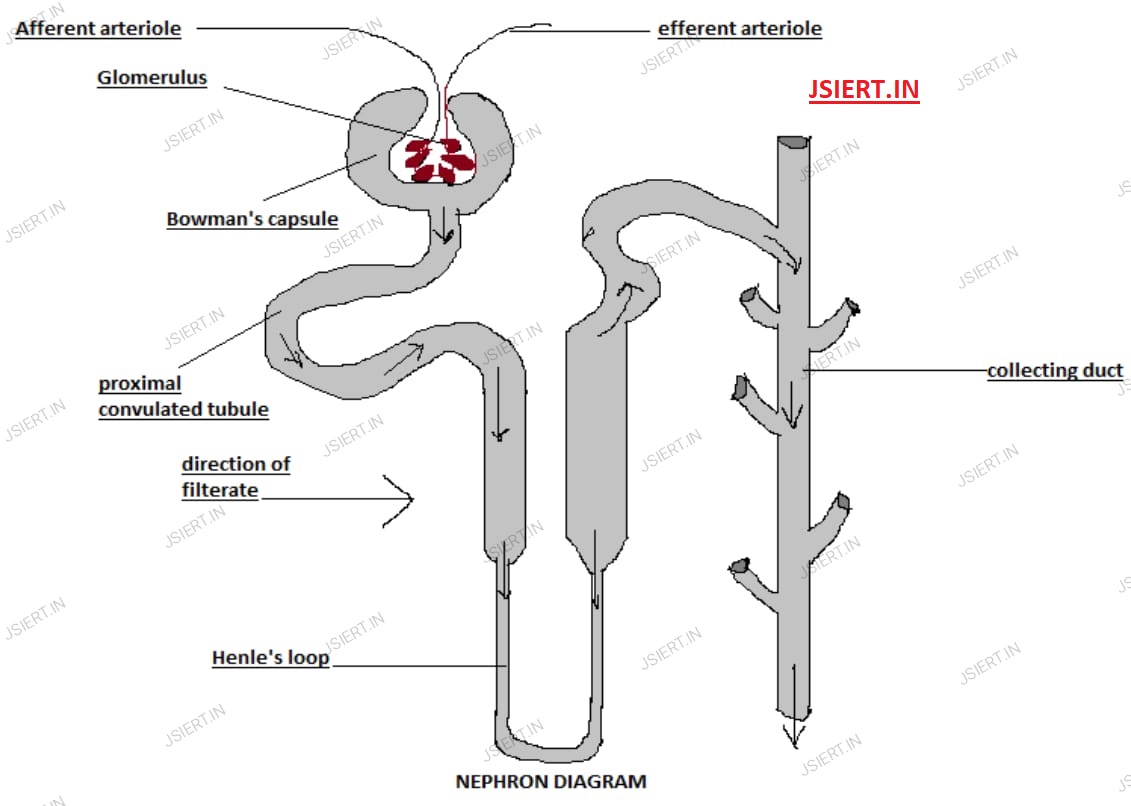
Functioning of Nephron
(i)Through the renal artery, which divides into numerous capillaries connected to the glomerulus, blood enters the kidney.
(ii) At Bowman\’s capsule, the water and solute are transported to the nephron.
(iii) Amino acids, glucose, and salts are selectively reabsorbed in the proximal tubule, while undesired molecules are added to the urine.
(iv) After that, the filtrate descends into the Henle loop, where more water is absorbed. The filtrate then ascends into the distal tubule and eventually reaches the collecting duct from this point. Numerous nephrons send urine to the collecting duct for collection.
(v) The ureter is a lengthy tube through which the urine produced by each kidney travels. It travels from the ureter to the urinary bladder and then enters the urethra.
