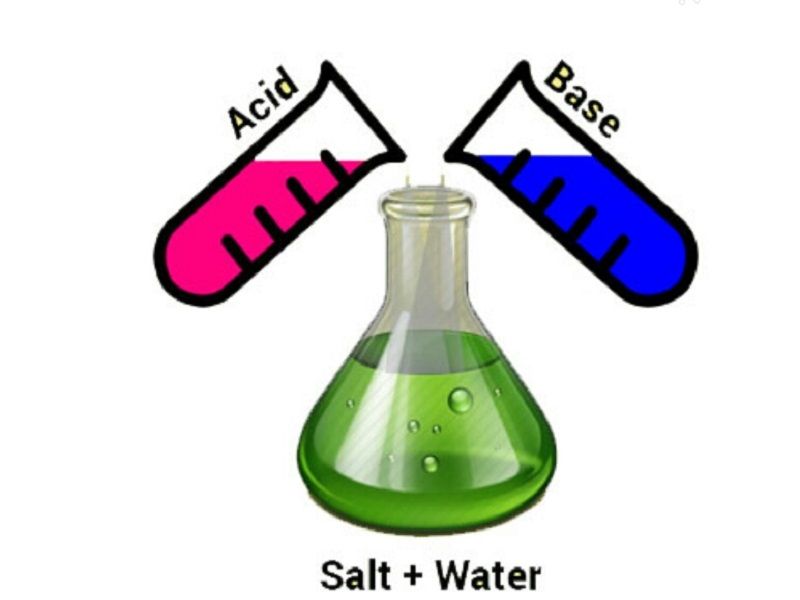
A neutralisation reaction is a chemical process in which an acid and a base combine to produce salt and water as the end products.
H+ ions and OH– ions combine to form water during a neutralisation reaction. Acid-base neutralisation is the most common type of neutralisation reaction.
As we have identified that all acids generate H+ (aq) and all bases generate OH– (aq) , we can view the neutralisation reaction as follows –
Neutralization Reaction Equation
Acid + Base (alkali) → Salt + Water
H X + M OH → MX + HOH
H+ ( aq ) + OH–( aq ) → H2O ( l )
