Introduction
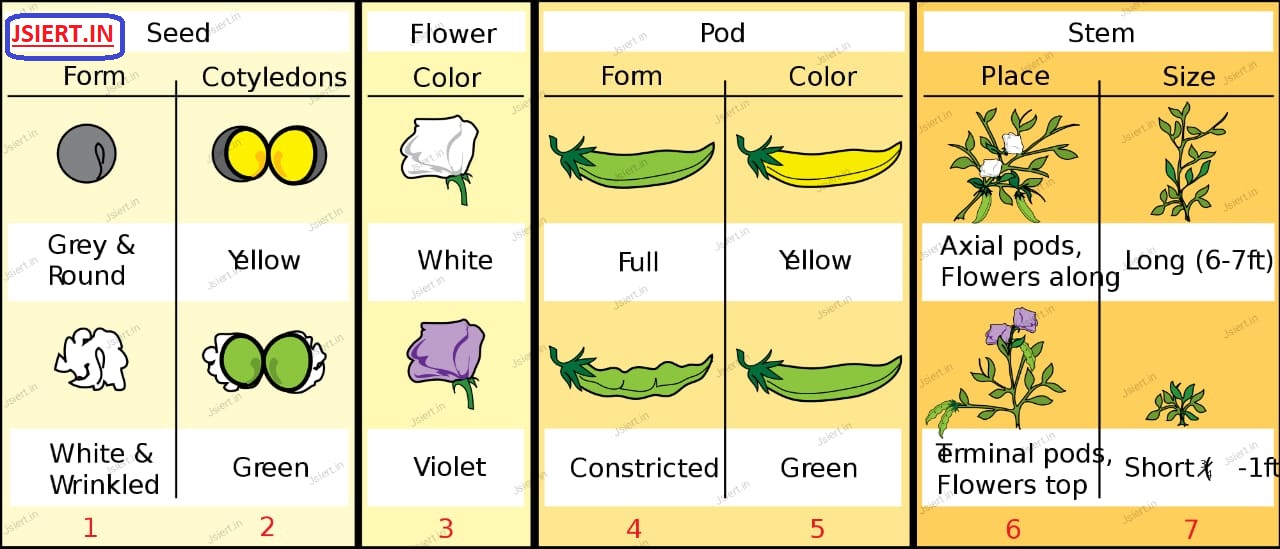
Mendel (1856-1863) conducted hybridization experiments on garden peas( Pisum sativum). During that period, he chose some characteristics of the peas and conducted some cross-pollination on the pea lines that showed stable trait inheritance and underwent continuous self-pollination.
Why was Pea Plant Selected for Mendel’s Experiments?
He selected a pea plant for his experiments for the following reasons:
(i)The pea plant can be easily grown.
(ii)They can also be cross-pollinated, they are naturally self-pollinated.
(iv)Due to the annual habit of the plant, multiple generations may be studied in less time.
There are many contrasting characters in it.
Mendel carried out two major experiments to determine the laws regarding inheritance.
These experiments included:
Monohybrid cross
Dihybrid Cross
Mendel determined through his experiments that some traits were constantly and slowly passed on to the progeny. These factors are now referred to as genes or hereditary units.
Mendel’s Experiment
Mendel conducted experiments on a pea plant and compared the features of the plants based on seven primary contrasts. Then, in order to determine the inheritance laws, he carried out both tests.