Plant hormone (phytohormone)
Organic compounds called as phytohormones are found in extremely small amounts in plants. They control the growth, reproduction, survival, and development of plants.
Let’s now examine the composition and uses of various phytohormones, like
(i) Auxins,
(ii) Gibberellins,
(iii) Cytokinins,
(iv) Ethylene, and
(v) Abscisic acid.
What are the main functions of plant hormones?
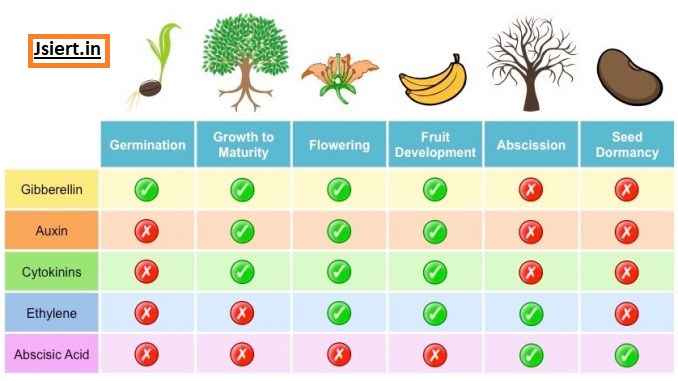
All of the growth and development activities, including cell division, enlargement, flowering, seed formation, dormancy, and abscission, are regulated by plant hormones.
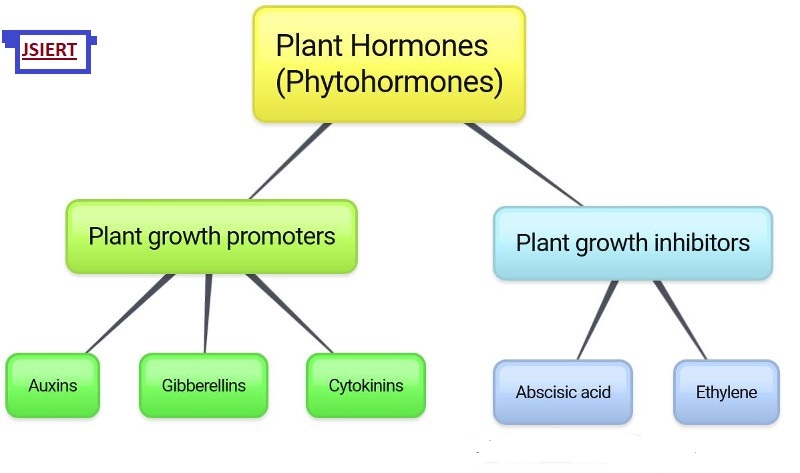
Plant hormones are divided into two categories based on how they act:
Plant Growth Promoters
Plant Growth Inhibitors.
(A) Auxin Hormone
Auxin means “to grow”. They are mostly used in agricultural and horticultural practices. They are found in the growing apex of roots and stems.
Natural: Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), Indole butyric acid (IBA)
Synthetic: 2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), NAA (Naphthalene acetic acid)
Functions of Auxin :
(i)The elongation of stem and root cells
(ii) IAA in the apical bud inhibits the growth of lateral buds due to apical dominance.
(iii) Causes parthenocarpy, which is the formation of fruit without fertilisation, as in the case of tomatoes.
(iv) Stops the early loss of leaves, flowers, and fruits.
(v) useful for grafting and stem cuttings where it starts the rooting process
(vi) promotes flowering, such as in pineapple
(vii) Extensive use of 2,4-D as a herbicide kills undesirable weeds of dicot plants without damaging monocot plants.
(B)Gibberellins Hormone
More than 100 gibberellins (GA1, GA2, GA3…..) are known. They are acidic. These are found in higher plants and fungi.
Functions of Gibberellins :
(i) promotes bolting, which is the sudden elongation of internodes in mound plants like cabbage and beets just before flowering
(ii) delays senescence
(iii) helps to parthenocarpy
(iv) stem elongation and dwarfism reverse
(v) allows certain plants, to become male
(vi) promotes the production of hydrolytic enzymes like amylase and lipase
(vii) Breaks seed dormancy.
(C) Cytokinins Hormone
In the process of cytokinesis, cytokinins are important. Plants that experience fast cell division, such as those with root apices, shoot buds, early fruits, etc., naturally produce cytokinins. Cytokinins migrate in a polar and basipetal manner.
Natural: Isopentenyl adenine, zeatin (corn kernels, coconut milk).
Synthetic: thidiazuron, kinetin, benzyladenine, and diphenylurea.
Functions of Cytokinins hormone:
(i) It is used to start shoot growth in culture and promotes lateral and adventitious shoot growth.
(ii) helps in combating auxin-induced apical dominance.
(iii) promote the growth of leaves’ chloroplasts
(iv) promotes the mobilisation of nutrients and delays leaf senescence.
(D)Abscisic Acid
It is a hormone that inhibits growth. GAs are counterbalanced by ABAs. It promotes dormancy and abscission by inhibiting plant metabolism. Because it raises plants’ stress tolerance, it is also known as “stress hormone.” Abscisic acid (ABA).
Functions of Abscisic acid:
(i)causes leaves and fruits to fall off
(ii) inhibits the germination of seeds
(iii) induces leaves to senesce
(iv ) accelerates dormancy in seeds, which is useful for storage.
(v) stimulates stomatal closure to prevent transpiration when there is a lack of water.
(E) Ethylene Plant Hormone
Both an inhibitor and a growth promoter, it works. takes the form of gas. It is created in tissues going through senescence and in ripening fruits. It is one of the most commonly utilised hormones in agriculture and controls a number of physiological processes.
Functions Ethylene Plant Hormone:
(i) It accelerates fruit ripening.
(ii) It accelerates fruit ripening. the epinasty of leaves.
(iii) Breaks seed and bud dormancy.
(iv) stimulates the rapid elongation of internodes and petioles.
(v) promotes leaves and flowers to senesce and die.
(vi) causes the production of root hair and root growth, increasing the absorption surface.
(vii) increases the female hormone in monoecious plants.
(viii) Formation of the apical hook in dicot seedlings.