The chemical formula of a compound is a symbolic representation of its composition. The chemical formulae of different compounds can be written easily. For this exercise, we need to learn the symbols and combining capacity of the elements.
The combining power (or capacity) of an element is known as its valency. Valency can be used to find out how the atoms of an element will combine with the atom(s) of another element to form a chemical compound.
The valency of the atom of an element can be thought of as hands or arms of that atom.
Human beings have two arms and an octopus has eight. If one octopus has to catch hold of a few people in such a manner that all the eight arms of the octopus and both arms of all the humans are locked, how many humans do you think the octopus can hold?
Represent the octopus with O and humans with H. Can you write a formula for this combination? Do you get OH4 as the formula?
The subscript 4 indicates the number of humans held by the octopus.
The valencies of some common ions are given below

The rules that you have to follow while writing a chemical formula are as follows:
• the valencies or charges on the ion must balance.
• when a compound consists of a metal and a non-metal, the name or symbol of the metal is written first. For example: calcium oxide (CaO), sodium chloride (NaCl), iron sulphide (FeS), copper oxide (CuO) etc., where oxygen, chlorine, sulphur are nonmetals and are written on the right,
whereas calcium, sodium, iron and copper are metals, and are written on the left.
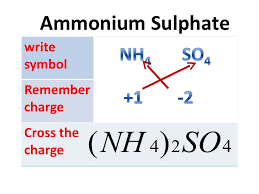
• in compounds formed with polyatomic ions, the number of ions present in the compound is indicated by enclosing the formula of ion in a bracket and writing the number of ions outside the bracket.
For example, Mg (OH)2
. In case the number of polyatomic ion is one, the bracket is not required. For example, NaOH
FORMULAE OF SIMPLE COMPOUNDS
The simplest compounds, which are made up of two different elements are called binary compounds. . You can use ions to write
formulae for compounds.
While writing the chemical formulae for compounds, we write the constituent elements and their valencies as shown below. Then we
must cross over the valencies of the combining atoms.
Examples
1 Formula of hydrogen chloride
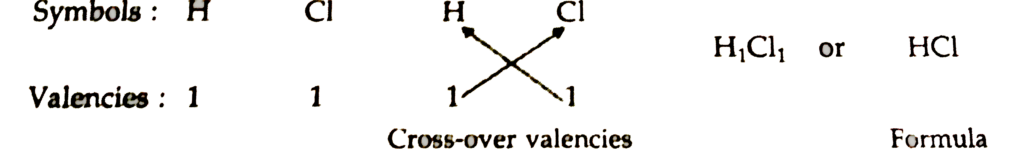
Formula of the compound would be HCl.
2 Formula of hydrogen sulphide

3 . Formula of carbon tetrachloride

For magnesium chloride, we write the symbol of cation (Mg2+) first followed by the symbol of anion (Cl– ). Then their charges are criss – crossed to get the formula.
4. Formula of magnesium chloride
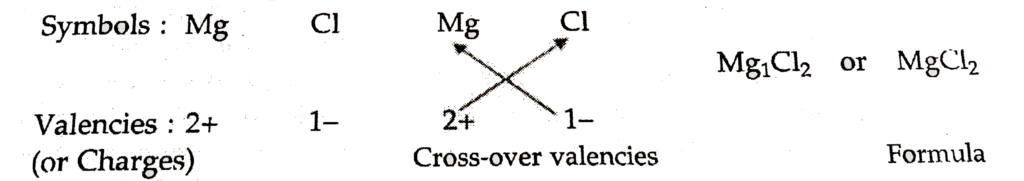
Thus, in magnesium chloride, there are two chloride ions (Cl– ) for each magnesium ion (Mg2+). The positive and negative charges must balance each other and the overall structure must be neutral. Note that in the formula, the charges on the ion.
Some more examples
(a) Formula for aluminium oxide:
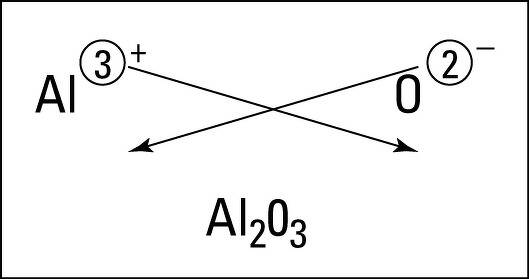
Formula : Al2O3
(b) Formula for calcium oxide
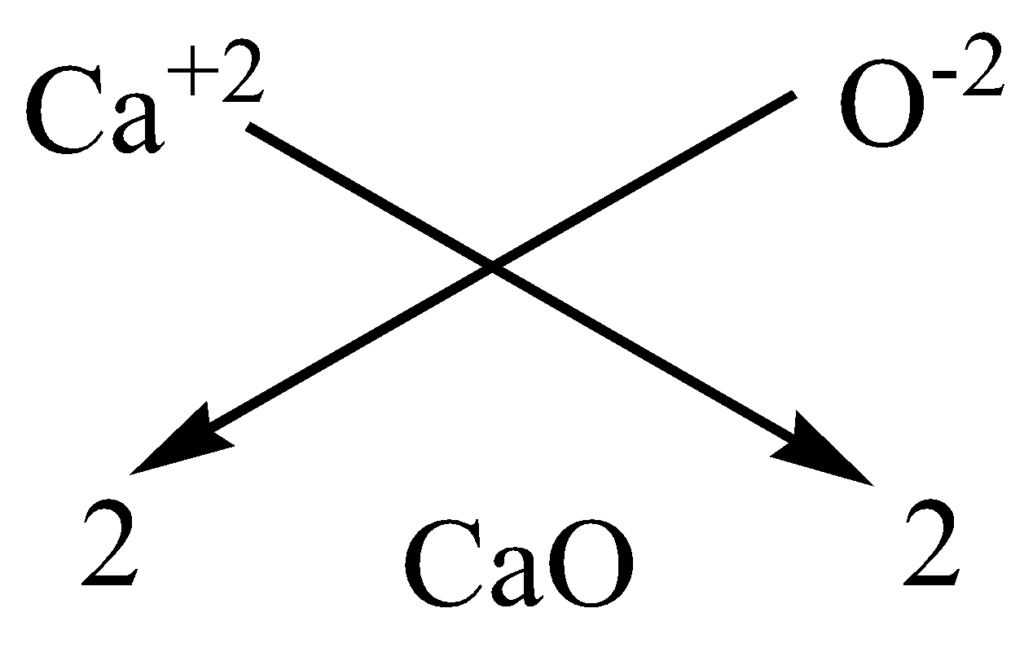
Here, the valencies of the two elements are the same. You may arrive at the formula Ca2O2.
. But we simplify the formula as CaO.
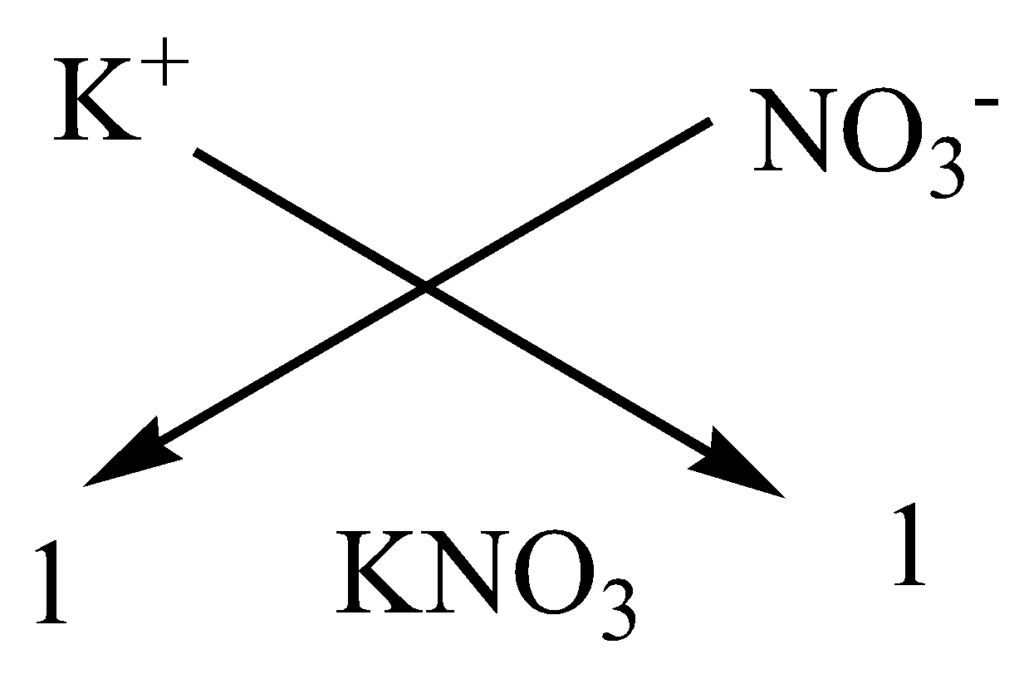
(c) Formula of Potassium nitrate:
(d) Formula of Magnesium hydroxide:
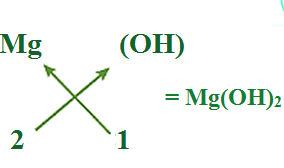
Note that the formula of calcium hydroxide is Mg(OH)2 and not MgOH2
. We use brackets when we have two or more of the same ions in the formula. Here, the bracket around OH with a subscript 2 indicates that there are two hydroxyl (OH) groups joined to one calcium atom. In other words, there are two atoms each of oxygen and hydrogen in Magnesium hydroxide.
(e) Formula of sodium carbonate:

In the above example, brackets are not needed if there is only one ion present.
(f) Formula of ammonium sulphate: